Golfer’s elbow, medically known as medial epicondylitis, is a common condition that affects the tendons on the inside of the elbow. While the name suggests it primarily impacts golfers, this condition can arise from various repetitive activities involving gripping, twisting, or bending movements of the wrist and forearm. Below is a comprehensive guide to understanding golfer’s elbow, its causes, symptoms, and treatments.
What is Golfer’s Elbow?
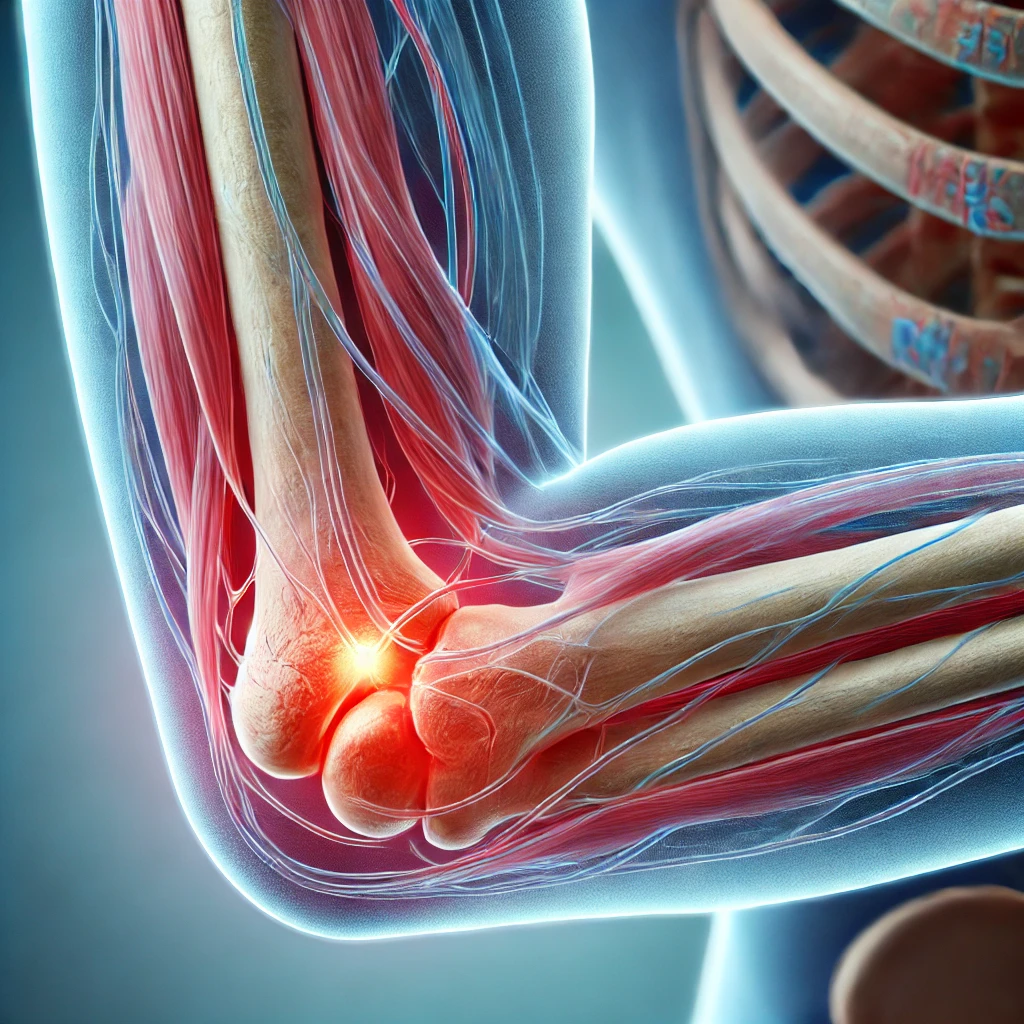
Golfer’s elbow is a form of tendonitis caused by overuse or strain on the forearm muscles that attach to the medial epicondyle (the bony bump on the inner elbow). These muscles are responsible for flexing the wrist and fingers. Repeated stress leads to microtears in the tendons, resulting in inflammation and pain near the elbow joint12.
Common Causes
Golfer’s elbow can develop from various activities beyond golfing. Common causes include:
- Sports-related movements: Pitching in baseball, serving in tennis (spin serves), or throwing javelins.
- Work-related tasks: Painting, hammering, typing, or using hand tools.
- Daily activities: Gardening, shoveling, raking, or carrying heavy objects like suitcases137.
Poor technique or unsuitable equipment (e.g., heavy tennis rackets or golf clubs) can exacerbate the condition23.
Symptoms
The hallmark symptom of golfer’s elbow is pain and tenderness on the inner side of the elbow. Other signs include:
- Pain radiating from the elbow to the wrist on the palm side.
- Weak grip strength or difficulty holding objects.
- Stiffness in the elbow joint.
- Worsened pain during wrist flexion against resistance or squeezing motions17.
Symptoms may develop gradually over weeks or months and can become chronic if left untreated7.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis typically involves:
- Physical examination: Doctors check for pain during wrist flexion against resistance.
- Imaging tests: X-rays rule out fractures or arthritis; MRIs may be used for unclear cases37.
Treatment Options
Treatment focuses on reducing pain and inflammation while promoting healing and preventing recurrence. Key approaches include:
Self-Care
- Resting the affected arm for 4–6 weeks to avoid aggravating symptoms7.
- Applying ice packs to reduce inflammation7.
Medical Interventions
- Anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) for pain relief17.
- Corticosteroid injections for severe cases (rare)1.
- Bracing or splinting to support the forearm muscles during recovery17.
Physical Therapy
Strengthening exercises and stretches targeting wrist flexor muscles are essential for recovery. For example:
- Wrist flexor stretches involve extending your arm with your palm facing upward and gently pulling your fingers downward with your opposite hand68.
Massage Therapy
Massage therapy plays a vital role in managing golfer’s elbow by:
- Reducing muscle tension through techniques like cross-friction massage49.
- Increasing blood flow to promote healing5.
- Breaking down scar tissue formed around injured tendons59.
- Using specialized methods such as deep tissue massage, active release technique, or myofascial release to alleviate pain and improve mobility910.
Massage therapists often combine soft tissue mobilization with passive stretching exercises for optimal results10.
Preventive Strategies
To prevent golfer’s elbow recurrence:
- Focus on improving technique in sports or work-related activities.
- Use ergonomic tools and equipment suited to your needs.
- Strengthen forearm muscles through targeted exercises.
- Gradually increase activity intensity to avoid overloading tendons.
Conclusion
Golfer’s elbow is a manageable condition with proper care and treatment. Whether you’re an athlete or someone engaged in repetitive manual tasks, understanding its causes and symptoms can help you seek timely intervention. Combining rest, physical therapy, massage techniques, and preventive measures ensures faster recovery and long-term relief from discomfort.
If you suspect golfer’s elbow, consult a healthcare provider or massage therapist for personalized care tailored to your needs.
Disclaimer: This content is for informational purposes only and is not intended to substitute professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.
Citations:
- https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/medial-epicondylitis-golfers-and-baseball-elbow
- https://sportsmedicine.mayoclinic.org/condition/golfers-elbow-medial-epicondylitis/
- https://www.folsomortho.com/golfers-elbow-orthopaedic-surgery-ca.html
- https://www.bobandbrad.com/post/how-to-heal-golfer-s-elbow-with-self-massage
- https://www.zoomershealth.ca/articles/how-massage-therapy-can-relieve-golfers-elbow/
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=COR8myESUWE
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/21711-golfers-elbow-medial-epicondylitis
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=H58FYW3WQ2I
- https://evergreenclinic.ca/how-can-massage-therapy-help-with-golfers-elbow/
- https://www.massagetherapyreference.com/golfers-elbow-massage/
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_PTfWWCuv5o
- https://medmassager.com/blogs/articles/massage-for-golfers-elbow
- https://ccoe.us/news/golfers-elbow/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK519000/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507002/
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/golfers-elbow/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20372872
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tK1SPKmOZzw
- https://www.physio-pedia.com/Medial_Epicondyle_Tendinopathy
- https://www.upmc.com/services/orthopaedics/conditions/golfers-elbow
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/golfers-elbow/symptoms-causes/syc-20372868
